Introduction
The Union-Find Disjoint Set (UFDS) is a data structure to model a collection of disjoint sets with the ability to efficiently determine which set an item belongs to in constant time. It is usually used to solve the problem of finding connected components in an undirected graph.
The process is begun with initialize every vertex to a separate disjoint set, then enumerate every edge in a graph (or every relationship between two vertices) and join every two vertices or disjoint sets. UFDS is designed to solve this. In C++, such structure is not efficiently supported in STL library. So we will implement it here.
The whole idea is above how to select a good representative ‘parent’ item to represent a set. We need to ensure that all vertices in one set all have one unique ‘representative’. The UFDS takes advantage of tree structures where the disjoint sets form a forest of trees. The root of one tree is picked to be the representative for all its descendants.
To achieve this, I will use std::vector<int> p to denote the parents and std::vector<int> rank to denote the height of a node.
Thus $p[i]$ stores the immediate parent of item $i$. $p[i] = i$ is true when item $i$ is a representative of a certain disjoint set. To union two disjoint sets,
we set the representative item (root) of one disjoint set to be the new parent of the representative item of the other disjoint set. After calling $unionSet(i, j)$
function, both item $i$ and $j$ will have the same representative item, directly or indirectly. During this process, we pick the mutual representative
based on the rank field values. Note that we always pick the one with higher rank to be the new parent of the disjoint set.
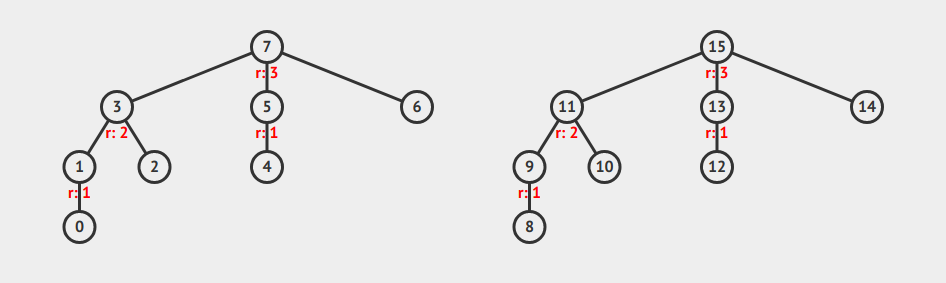
There is also one technique called Path Compression, which is used to vastly speed up the $findSet(i)$ function. This is done by setting the parent of all items traverse to point directly to the root. Any subsequent calls to $findSet(i)$ on the affected items will then result in only one link being traversed.
Implementation
#ifndef __UFDS
#define __UFDS
#include <vector>
class UnionFind{
private:
std::vector<int> p, rank;
public:
UnionFind(int N){
rank.assign(N,0);
p.assign(N,0);
// initialize every node to point to themselves
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) p[i] = i;
}
int findSet(int i){ return (p[i] == i) ? i : (p[i] = findSet(p[i])); }
bool isSameSet(int i, int j){return findSet(i) == findSet(j); }
void unionSet(int i, int j){
if( !isSameSet(i, j)){
// find their representatives
int x = findSet(i), y = findSet(j);
// compare ranks and prefer higher one
if(rank[x] > rank[y]) p[y] = x;
else{
p[x] = y;
// if they have the same rank, increment the root's rank
if ( rank[x] == rank[y] ){
rank[y]++;
}
}
}
}
};
#endif



Leave a Comment